The Dangers of Prolonged Sitting: How It Affects Your Health and How to Reduce Its Impact

In today’s modern world, many of us spend long hours sitting in front of a computer for work, entertainment, or other activities. Even during transportation. This prolonged sitting has become a common habit across all age groups. As this trend grows, researchers are increasingly studying its potential harms and effects on our health.
In this article, we will explore some of the health risks associated with long periods of sitting and how to mitigate them.
Spinal Problems
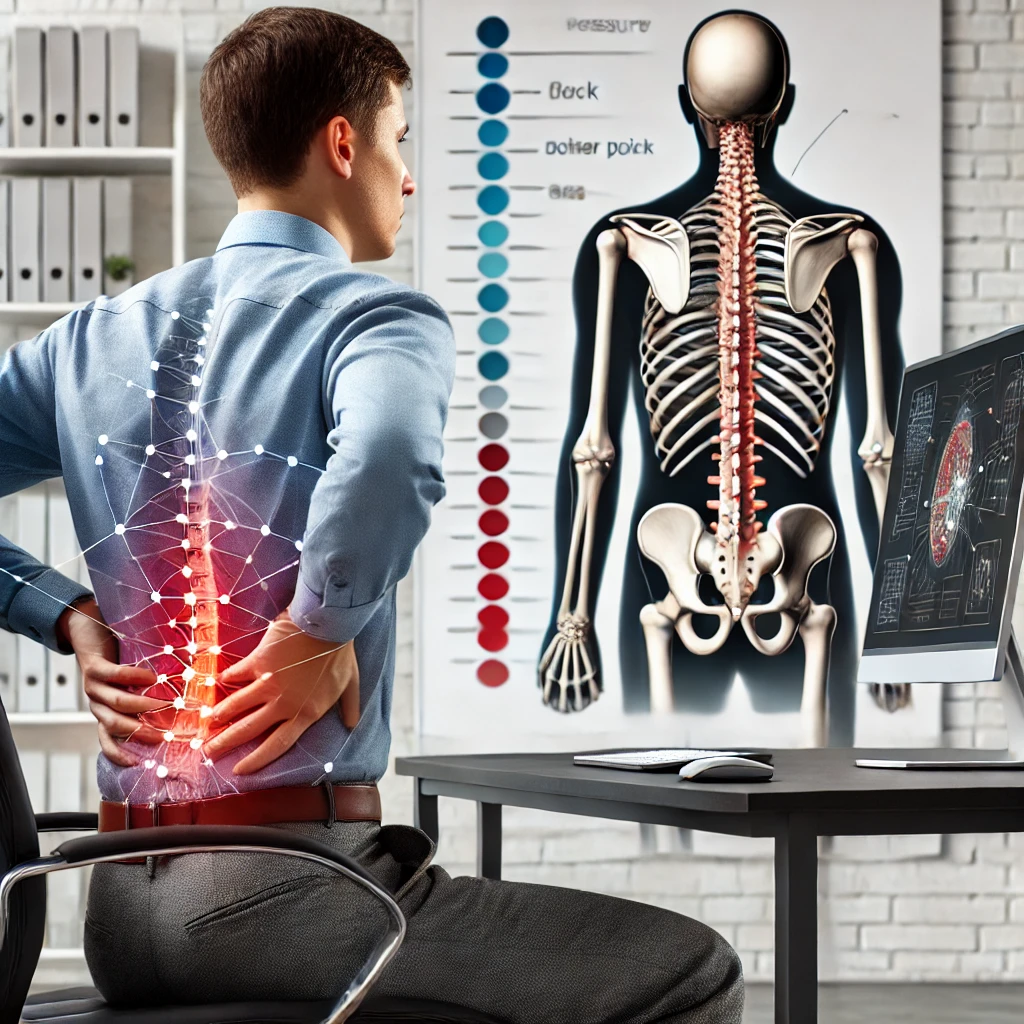
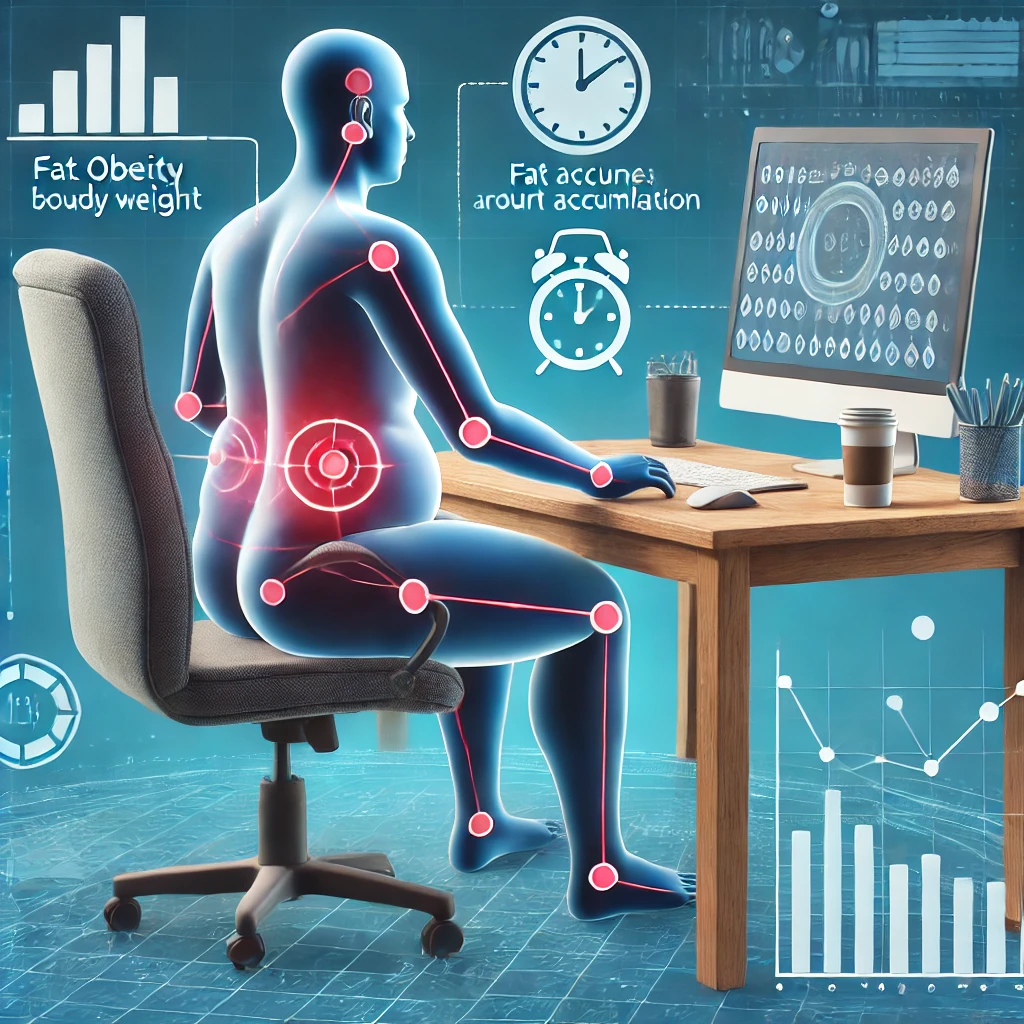
One of the most significant risks of prolonged sitting is related to spinal health. Poor posture during long sitting sessions can lead to conditions like scoliosis, or spinal curvature. When sitting for extended periods in improper positions, uneven pressure is placed on the spine, causing unnatural curvatures in the back. This can lead to stiffness in the shoulders and neck due to constant pressure on the muscles.
Additionally, prolonged sitting increases pressure on the spinal discs, especially in the lower back, leading to herniated discs. These issues are more common as people age, with spinal discs losing flexibility and becoming more prone to wear and tear. According to a study published in the American Journal of Epidemiology, prolonged sitting is linked to an increased risk of spinal and musculoskeletal issues, highlighting the importance of regular movement and adjusting sitting posture.
Muscle Weakness
Muscle weakness is another direct consequence of physical inactivity caused by prolonged sitting. Over time, essential muscles like those in the abdomen and back become inactive and lose strength. The legs also experience significant reduction in activity, which increases the risk of muscle atrophy.
Muscle atrophy occurs when muscles are not regularly used, leading to gradual loss of muscle mass, affecting balance and mobility. This issue is particularly evident in people who spend long hours sitting at desks or using electronic devices. The American Physical Therapy Association emphasizes that regular movement and exercise are crucial for maintaining muscle strength and preventing atrophy.
Poor Circulation in the Legs
Experiencing pain or discomfort in the legs after sitting or standing for long periods may indicate a condition known as chronic venous insufficiency, where fluid builds up in the veins of the legs. According to the Mayo Clinic, this condition may become a concern if accompanied by swelling or other symptoms.
This issue closely resembles the common occurrence of swollen legs and feet during long flights. The main cause of this is sitting for prolonged periods without movement. When the feet remain on the ground for too long, blood pools in the veins of the legs. This position puts additional pressure on the veins, causing fluid to leak into the surrounding tissues, leading to swelling.
To reduce leg swelling and lower the risk of blood clots, it is recommended to wear compression socks during extended sitting periods, as they help improve blood flow by applying pressure to the lower legs.
Weight Gain and Obesity
Sitting for long periods in front of a computer significantly reduces the body’s ability to burn calories, contributing to a slower metabolism. This decrease in calorie burn increases the likelihood of weight gain, which can open the door to chronic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease.
On the other hand, even minimal physical activity can have a big impact. Physical movement helps burn more calories, leading to weight loss and increased energy levels. Regular activity also improves muscle strength, enhances mobility, and has a positive impact on mental health, especially as we age.
Research shows that prolonged sitting is associated with several health issues, including obesity, high blood pressure, increased blood sugar levels, abdominal fat accumulation, and elevated levels of unhealthy cholesterol.

Mental and Emotional Impact
Studies have shown that sitting for long periods can increase the risk of developing anxiety and depression. When physical activity decreases, the hormones that regulate mood, such as serotonin and endorphins, are affected. Thus, engaging in activities like walking or exercising can improve mood and overall mental well-being.
I hope this post has been informative and helpful in understanding the health risks associated with prolonged sitting and how to mitigate them. If you’re interested in learning more about staying healthy, be sure to check out my latest post here.
Curious about exploring the best ergonomic chairs on the market? Check out our full collection of ergonomic chairs for more options tailored to your gaming and comfort needs.
Looking for in-depth insights on the top chairs available? Take a look at our comprehensive chair reviews to help you make the right choice.



